The term “propaganda” is often thrown around, but what exactly does it entail? From politics to advertising, propaganda is a pervasive force that shapes our thoughts and beliefs.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the depths of propaganda, unraveling its purpose, the various types it takes, and the methods through which it is disseminated. We’ll also explore the telltale signs of propaganda and equip you with strategies to safeguard yourself against its influence.
What Is Propaganda?
In its broadest sense, propaganda is a systematic effort to manipulate and shape people’s understanding, emotions, and actions through various forms of communication.
This can manifest in different forms, such as biased or misleading information, selective use of facts, and persuasive language to influence public opinion. The impact of propaganda on information can distort reality and manipulate perceptions, thereby shaping the narrative around a particular issue. It plays a pivotal role in communication and persuasion, often employed by governments, organizations, or individuals with specific agendas.
Whether through mass media, social media, or interpersonal communication, propaganda can sway opinions and behaviors, making it a potent tool for influencing public discourse.
Read Also:- Risk Mitigation
Why Is Propaganda Used?
Propaganda is used for various purposes, including shaping understanding, controlling information, influencing persuasion, and exerting power over individuals and societies.
It plays a significant role in media by molding public opinion, reinforcing ideologies, and framing narratives. In politics, propaganda is often employed to sway voters, discredit opponents, and boost the image of political parties or leaders. In advertising, it is harnessed to create consumer demand, establish brand identity, and manipulate perceptions.
Propaganda involves the skillful use of language, imagery, and psychological tactics to elicit specific responses, ultimately influencing behavior and societal attitudes.
What Are The Main Goals Of Propaganda?
The main goals of propaganda are to shape understanding, influence persuasion, exert power, and mold cultural and societal values through strategic messaging targeted at specific audiences.
This deliberate dissemination of information aims to sway public opinion towards a particular ideology, belief system, or political agenda. Propaganda leverages various mediums, such as media, art, and advertising, to establish a dominant narrative and maintain social control. It is instrumental in steering collective attitudes, fostering allegiance, and bolstering the authority of ruling entities. Ultimately, propaganda plays a pivotal role in shaping a society’s mindset, perpetuating cultural norms, and reinforcing the influence of those in power.
What Are The Different Types Of Propaganda?
Propaganda takes on various forms and faces, employing psychological manipulation and specific techniques and tactics to achieve its objectives.
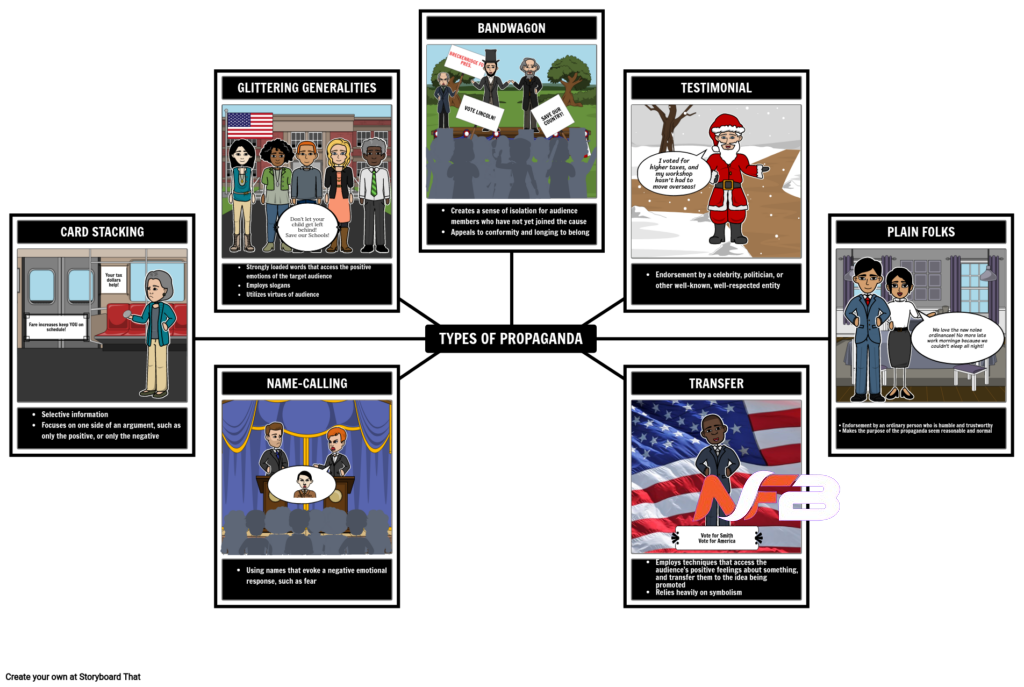
Whether it’s the use of fearmongering to instill anxiety and compliance or the strategic dissemination of biased information to shape public opinion, propaganda manifests itself in diverse ways. From the subtle persuasion in advertising to the overt manipulation in political rhetoric, the impact of propaganda is far-reaching. It thrives on the art of influence, utilizing visuals, language, and emotion to sway individuals and societies.
Understanding the complexities of propaganda requires awareness of its multifaceted nature and the underlying strategies it employs.
White Propaganda
White propaganda involves disseminating information with transparency about its sources, aiming to influence messaging and shape perceptions through strategic manipulation.
This form of propaganda often uses credible sources, such as experts, scholars, or reputable organizations, to convey its message. The goal is not to deceive but to subtly influence public opinion in favor of a particular idea, cause, or agenda. By presenting information seemingly objectively, white propaganda can be more persuasive, as it may be viewed as reliable and trustworthy.
It’s essential to be aware of the potential biases and motives behind the information presented in white propaganda to evaluate its validity and implications critically.
Black Propaganda
Black propaganda operates through the deliberate spread of misinformation and disinformation to distort truth and manipulate perceptions through deceptive tactics.
Black propaganda often aims to sow seeds of doubt, create confusion, and incite fear among the targeted audience. By leveraging false narratives, fabricated evidence, and anonymous sources, it seeks to erode trust and credibility. This form of propaganda can be disseminated through various channels, including social media, fake news websites, and anonymous leaflets, making it difficult to trace its origins. Its impact can be far-reaching, influencing public opinion, shaping political discourse, and even inciting conflict.
Grey Propaganda
Grey propaganda blurs the line between truth and misinformation, aiming to influence perception and bias by strategically disseminating ambiguous information.
This form of propaganda often operates through channels not attributable to a specific source, making it challenging for audiences to discern the true origins and intentions behind the information. It leverages subtle manipulation techniques to sway public opinion, often by insinuating doubt or creating confusion. By exploiting uncertainty, grey propaganda can shape narratives in line with its agenda, ultimately impacting public perception and fostering bias without overtly revealing its underlying motives.
Red Propaganda
Red propaganda is intricately linked to political objectives. It aims to influence societal and cultural values through strategic manipulation and messaging within political contexts.
It often operates by disseminating biased information, utilizing emotionally charged language, and distorting facts to shape public opinion in favor of specific political ideologies or agendas. Red propaganda can be found in various forms, such as state-sponsored media, stirring up nationalistic fervor, and demonizing opposition parties or foreign entities. Its existence can significantly impact public perception, sway elections, and mold public policy, leading to far-reaching consequences in a nation’s cultural and social fabric.
Blue Propaganda
Blue propaganda focuses on shaping communication, influencing persuasion, and exerting influence through strategic manipulation targeted at specific audiences and contexts.
It significantly shapes public attitudes toward certain ideologies, products, or individuals. By utilizing various communication channels such as social media, advertising, and public relations, blue propaganda seeks to sway the thoughts and emotions of its intended audience. This propaganda often employs subtle messaging and imagery to create a favorable perception while discrediting opposing viewpoints. The ultimate goal is to establish a sense of trust and loyalty to a particular message or entity.
How Is Propaganda Spread?
Propaganda spreads through various channels, including media manipulation, psychological tactics, and strategic communication to influence and shape perceptions.
These propaganda methods are often employed to sway public opinion, control narratives, and promote specific agendas. Media manipulation involves selectively presenting information, framing, or even fabricating stories to sway the audience’s beliefs. Psychological tactics tap into emotions and subconscious triggers to create a desired response. Meanwhile, strategic communication utilizes influential platforms and targeted messaging to amplify a particular perspective. By incorporating these multifaceted approaches, propagandists aim to mold individuals’ thoughts and beliefs, ultimately shaping societal attitudes and behaviors.
Media Manipulation
Media manipulation is crucial for propagandistic spread, influencing information, shaping societal values, and exploiting bias within targeted audiences.
It is pivotal in shaping public opinion, particularly in political contexts. Through selective framing and messaging, media manipulation can sway public perception, perpetuate stereotypes, and incite fear or anger. This can have far-reaching implications, as it affects not only individual beliefs and behaviors but also the functioning of a democratic society.
The impact of media manipulation is significant, as it can fuel misinformation, polarize communities, and contribute to the erosion of trust in journalistic institutions.
Psychological Manipulation
Psychological manipulation is critical to propagandistic spread. It targets influence, shapes communication, and employs specific tactics to achieve its objectives.
It plays a pivotal role in shaping public opinion, instilling fear, or creating a sense of urgency to persuade individuals to align with particular ideologies or agendas. By utilizing tactics such as selective exposure, framing, and fear appeals, psychological manipulation can exploit cognitive biases and emotional triggers, influencing individuals to accept or reject specific ideas. It underlines the power dynamics in communication, emphasizing manipulating information flow to sway perceptions and behaviors, ultimately shaping society’s collective mindset.
Word of Mouth
Word of mouth is an organic yet influential method for propagandistic spread, impacting information dissemination, societal beliefs, and individual influence.
Word of mouth has immense power in shaping public opinion, as personal recommendations and testimonials often resonate more deeply with individuals than traditional advertising. Word of mouth can swiftly amplify or discredit narratives in tightly-knit communities, forming collective beliefs.
The digital age has magnified its impact, with social media platforms enabling rapid dissemination of information through user-generated content. Consequently, word of mouth plays a pivotal role in perpetuating or challenging propaganda, bearing significant societal implications.
What Are The Signs Of Propaganda?
Identifying propaganda involves recognizing signs such as:
- Emotional appeal
- Demonization of opponents
- Simplification of complex issues
- The use of loaded language to manipulate perceptions
These signs often aim to sway individuals’ beliefs through emotions rather than logic. Emotional manipulation is pivotal in attracting sympathizers to a particular cause or idea, often by exploiting fear, love, anger, or other strong emotions.
Demonization is used to paint opponents as evil or immoral, creating a clear ‘us versus them’ narrative. Complex issues are distilled into black-and-white scenarios, oversimplifying the reality to make aligning with the propagandist’s agenda easier. Loaded language provokes solid emotional responses and evokes unwavering support for a specific viewpoint.
Emotional Appeal
Emotional appeal is a prominent sign of propaganda. It seeks to manipulate and influence through emotional cues, shaping persuasion and exploiting bias within audiences.
This strategy influences people’s emotions, fostering a sense of attachment or fear to sway opinions. By tapping into deep-seated feelings, propaganda can stir up intense responses that override logical judgment. This often leads individuals to adopt beliefs and take actions aligned with the propagandist’s agenda. Thus, emotional appeal in propaganda is a powerful tool for molding perceptions and guiding behavior, effectively leveraging human tendencies for emotional responsiveness.
Demonization of Opponents
Demonizing opponents is a clear sign of propaganda, which aims to manipulate perceptions, influence attitudes, and shape societal dynamics by portraying adversaries negatively.
This tactic creates an ‘us versus them’ mindset, fostering community hostility and division. By presenting opponents as malevolent and threatening, propaganda diminishes the likelihood of reasoned discourse and empathy, fuelling polarization.
Propaganda can fuel prejudices and deepen societal rifts, obstructing constructive dialogue and understanding. This divisive tactic can undermine social cohesion and set the stage for contentious, polarized environments, ultimately impacting the fabric of society.
Simplification of Complex Issues
The simplification of complex issues is a telling sign of propaganda, which aims to manipulate information, influence perceptions, and shape societal understanding through oversimplification.
When complex topics are oversimplified, essential nuances and intricacies are often disregarded, leading to a distorted representation of reality. This can profoundly impact people’s perceptions and understanding of crucial matters, ultimately serving the interests of those propagating the simplified narrative. By breaking down intricate issues into easily digestible fragments, propagandists can sway public opinion and reinforce specific ideologies, thereby molding the collective consciousness.
The oversimplification of complex matters can ingrain specific perspectives, shaping how individuals interpret and engage with the world around them and perpetuating an environment conducive to sway and influence.
Use of Loaded Language
Using loaded language is a prominent sign of propaganda, aiming to manipulate communication, shape messaging, and influence perceptions through strategically crafted language.
Loaded language’s manipulative nature is evident in its ability to sway public opinion, create emotional responses, and solidify certain beliefs or ideas by employing carefully selected words and phrases. Such language can induce fear, prejudice, or biased thinking, subtly guiding individuals toward predetermined attitudes and stances.
In communication, loaded language wields significant power, as it can effectively influence how the audience receives, processes, and interprets information.
How Can Someone Protect Themselves From Propaganda?

Protecting oneself from propaganda involves critical strategies such as:
- By fact-checking sources, individuals can verify the accuracy of information.
- Understanding biases helps in recognizing and filtering out one-sided or misleading content.
- Cultivating critical thinking equips individuals to question, analyze, and assess information before believing or sharing it.
- Diversifying sources of information ensures exposure to varied perspectives, thus reducing the susceptibility to being influenced by a single narrative.
These measures collectively fortify individuals against the deceptive nature of propaganda.”
Fact-checking Sources
Fact-checking sources serves as a crucial protective strategy against propaganda. It empowers individuals to verify information and cultivate critical thinking to counter manipulative tactics.
It plays a significant role in enabling people to discern the reliability of information by scrutinizing sources and evaluating their credibility. Through fact-checking, individuals can cross-reference data, detect misinformation, and mitigate the potential spread of misleading content. This process fosters a culture of critical analysis, enabling individuals to approach information with a discerning eye and resist falling prey to deceptive narratives.
By consistently fact-checking sources, one can contribute to upholding the integrity of information dissemination and combating the proliferation of propaganda.
Being Aware of Biases
Understanding and being aware of biases is a fundamental protective measure against propaganda, allowing individuals to discern manipulative tactics, shape perceptions, and seek truth amidst biased information.
By acknowledging and addressing personal biases, individuals can develop a critical lens through which they assess information, reducing susceptibility to manipulation and deception. Bias awareness enables people to recognize how propaganda can infiltrate their perceptions, encouraging a more discerning approach to media and communication.
This heightened consciousness about biases fosters a commitment to truth-seeking, fostering a society better equipped to decipher the complexities of information and distinguish between fact and fiction.
Critical Thinking
Cultivating critical thinking is a pivotal protective measure against propaganda. It enables individuals to analyze manipulative tactics, question societal and cultural influences, and discern truth amidst persuasive messaging.
By honing critical thinking skills, people can recognize emotional appeals, logical fallacies, and distorted information disseminated through various mediums. This discerning approach protects against being swayed by biased narratives, political agendas, and commercial interests.
Individuals with critical thinking skills are better equipped to appreciate the complexity of societal and cultural influences and recognize the impact of historical context, power dynamics, and socio-economic factors on the dissemination and reception of information.
Diversifying Sources of Information
Diversifying sources of information acts as a strategic protective measure against propaganda, enabling individuals to broaden their perspectives, counter manipulative perceptions, and strengthen their communication insights.
By accessing information from various reputable sources, individuals can develop a more comprehensive understanding of complex issues, reducing the risk of falling victim to biased or fabricated content. This approach fosters critical thinking, enhances media literacy, and promotes informed decision-making.
Diversified sources empower individuals to discern between credible information and disinformation, fostering a more discerning and discerning approach to processing and disseminating information.
Read Also:- Self-Control is Strength, Calmness is Mastery – TYMOFF










Leave a Reply