Almost all office equipment needs stable and high-quality internet – PCs, laptops, printers, MFPs, IP phones, and other devices. If a company experiences network problems, work can come to a halt. Not only speed is important, but also the number of simultaneously connected devices, coverage area, and the possibility of wired connection. Let’s discuss how to choose a suitable model for the office: which characteristics are important and how they affect performance.
What is a Router and How Does it Work
Most often, high-speed internet is brought to the office via cable and connected to a router. It’s needed to transmit internet from the provider to connected devices.
Most routers have several ports to which office equipment can be connected via cable.
If the router has a wireless connection function, it converts the internet signal into radio waves – this is how Wi-Fi is created. The client device catches the wave, receives data, and sends it back. This article will focus on choosing a Wi-Fi router.
What are Wi-Fi Standards
Standards define the basic capabilities of the network, including data transmission speed and router range. The more modern the standard, the higher the performance characteristics.

Main Wi-Fi standards:
- 802.11n (Wi-Fi 4) – works in 2.4 and 5 GHz bands, throughput up to 600 Mbps;
- 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) – 2.4 and 5 GHz, up to 6.77 Gbps;
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6) – 2.4 and 5 GHz, up to 11 Gbps. Standards are indicated on the router box.
What to Consider When Choosing
Routers supporting Wi-Fi 6 are the most advanced. But when buying, you need to consider the capabilities of office equipment. You can connect devices with an outdated standard to a more modern router, but the internet speed will correspond to the old standard, not the new one.
What Affects Network Coverage Area
Various factors affect the quality and coverage area of Wi-Fi. For example, interference from other devices that distribute wireless internet, and obstacles: furniture, walls, and ceilings. The more obstacles in the signal’s path, the smaller the coverage area and the worse the network quality. The following router characteristics help achieve a stable network signal.
Operating Range
Routers exchange information with devices using radio waves of a certain frequency – this is called the device’s operating range. Modern routers can work in two frequency bands – 2.4 and 5 GHz.
2.4 GHz frequency.
At this frequency, the wave is less sensitive to interference, so it passes better through various obstacles, and the coverage area is larger. This range is the most popular, often used by default. If the office has neighbors, they also use Wi-Fi routers. Several devices clog the channel and create interference for each other, so the signal quality drops.
5 GHz frequency.
In this frequency operating range, the coverage area is smaller. Usually, you can achieve a quality connection only within one room or a small space. This is due to the peculiarities of wave attenuation and its sensitivity to obstacles. The communication channel at 5 GHz is wider, so the data transfer speed is higher. Additionally, this frequency range is not used as often, meaning interference from other devices is less noticeable.
What to Consider When Choosing
It’s better to buy a router that works in two ranges. Some devices have a function of automatically switching between frequencies depending on network conditions. For example, if the 2.4 GHz range is too congested, the router will switch to 5 GHz. But keep in mind that not all client devices support operation at this frequency.
Transmitter Power
The higher the transmitter power in the router, the stronger the signal and the further it spreads. If you need to connect a large number of devices to the internet or organize Wi-Fi in a large office, it’s better to choose devices with more powerful transmitters.
What to Consider When Choosing
Transmitter power is limited by technical requirements for radio frequencies: it should not exceed 24 dBm. The same solution sets limitations on transmitter power in client devices: no more than 20 dBm. Therefore, even if you install a router with the most powerful transmitters, this won’t always solve the problem of expanding the coverage area.
Antenna Type and Gain
Antennas are needed to direct radio waves. They can be directional or omnidirectional. Directional antennas transmit signals in only one direction. They are used when you need to cover a specific remote area with a network, such as a nearby parking lot. Omnidirectional antennas transmit signals in all directions, so they should be installed in the center of the room.
An important parameter is the antenna gain, measured in dBi. The higher it is, the further the wave travels.
What to Consider When Choosing
The antenna gain increases the signal range but makes it narrowly directional. This solution is suitable for a large office located on one floor, where device locations are known and static.
What’s Important for Internet Speed
Provider Speed
The actual router speed is usually lower than what is stated in its characteristics. This is because it’s limited by the provider’s capabilities. So, if the wired internet speed is 50 Mbps, the internet access speed won’t be higher, even if the router is rated for 300 Mbps.
Typically, internet from the provider is connected via cable through the WAN port.
What to Consider When Choosing
The port’s throughput is important. For high-speed tariffs, models with a throughput of at least 1 Gbps will be needed.
LAN Port
Many devices support Wi-Fi, but wireless networks are vulnerable to interference. Therefore, to achieve high data transfer speeds, it’s sometimes necessary to directly connect equipment to the network. For example, it’s recommended to connect servers only via cable.
For this purpose, almost all router models are equipped with LAN ports – connectors for wired device connection. Direct connection provides a more stable signal and high data transfer speed.
What to Consider When Choosing
Here, the port’s throughput is important: if the router is equipped with a gigabit network output, the data transfer speed increases significantly. It’s worth determining in advance how many devices you plan to connect via cable, as this affects how many connectors you’ll need.
MIMO Mode
MIMO is a signal coding method that allows increasing the data transfer speed to multiple devices using an antenna system.
The device manual usually indicates which scheme the router works on. For example, the MIMO 2×2 scheme means that two antennas receive the signal and two transmit. Schemes can be different: 1×2, 3×3.
What to Consider When Choosing
The more receiving antennas the router has, the higher the device’s sensitivity and data transfer speed.
What You Need to Know About Security
Devices connected to an unsecured network become vulnerable to cybercriminals. Malefactors can steal passwords from email and cloud storage, gain access to documents, or simply use the communication channel for their own purposes, degrading its performance.
Therefore, an office router must support modern encryption protocols. They provide protection for the wireless network and secure data transmission, as all processes are presented in the form of ciphers and codes. The more complex the protocol, the lower the probability of hacking.
Most routers support WPA2-PSK (TKIP), WPA2-PSK (AES), and WPA2-PSK (TKIP/AES) protocols, which almost completely protect the network from web attacks. The main thing is to use a complex password. Many modern devices support the new, even more secure WPA3 protocol. WEP is considered outdated and is relatively easy to hack using hacker key selection methods.
For additional data protection, you can create a guest network, disable WPS (password-free network access), and use a VPN (virtual private network).
What Else is Important When Choosing a Router
Presence of a USB port. Its functions:
- Connecting a 3G/4G modem as a backup communication channel during main line interruptions;
- Connecting a network printer; Connecting a webcam for surveillance;
- Updating router software from an external USB drive;
- Creating an FTP server.
Additional options for office work:
- Content filter (blacklist and whitelist). Allows blocking access to unwanted sites so employees don’t get distracted from work.
- IPTV. This is the ability to watch TV channels via the internet, which can be useful in the reception guest area.
Which Router to Choose
The choice of router is influenced by the number of connected devices, the area of the room, and its layout. Let’s consider two successful routers:
MikroTik hAP ac3
MikroTik hAP ac3 is a wireless dual-band router that sets new standards for home access points. This modern and affordable router
MikroTik hAP ac3 is characterized by high performance and attractive design, making it an ideal choice for homes of various sizes. One of the distinctive features of hAP ac3 is reliable dual-band wireless communication. This advanced technology ensures seamless network operation. Simultaneous coverage of both frequency bands optimizes overall performance and solves major problems related to interference in crowded places. hAP ac3 allocates a separate 5 GHz channel for modern devices, providing high-speed connection. At the same time, the 2.4 GHz channel provides reliable connection for older devices.
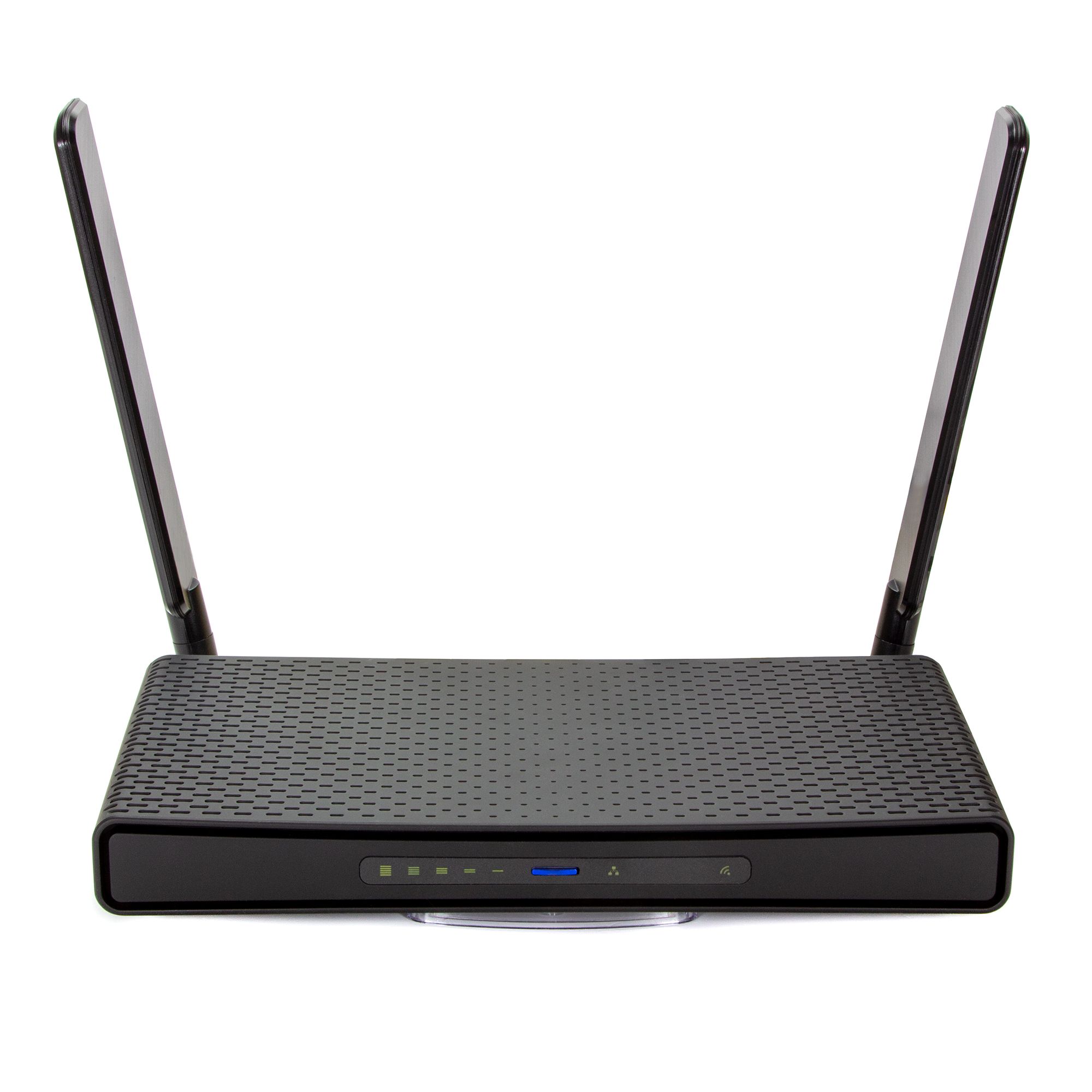

MikroTik hAP ax3
In 2023, MikroTik introduced a series of home Wi-Fi routers hAP ax, supporting Wi-Fi 6 technology. The series is designed for small homes, apartments, and small offices and offers a range of models meeting various requirements. The routers provide higher speed and enhanced signal in the 2.4 and 5 GHz spectrum. hAP ax devices are equipped with modern processors, large memory capacity, and several Ethernet ports, ensuring uninterrupted and reliable communication. Thanks to support for advanced encryption algorithm, routers in this series are distinguished by an increased level of security. Overall, hAP series routers provide high performance, scalability, and affordability for home networks.
What is a Mesh System and Why is it Needed
If you need to organize Wi-Fi in a large office with load-bearing brick or concrete partitions, connect a large number of devices. Mesh systems will come to the router’s aid.
They consist of several routers that receive and retransmit the signal from the main device (gateway) connected to the modem. Mesh systems distribute Wi-Fi signals from several points, so the internet speed is higher with them, the coverage area is wider, and the connection is more stable.
Final Conclusions
- A router receives a signal from the internet provider and transmits it to all connected devices in the office. It connects laptops, tablets, smartphones, MFPs, smart TV screens, surveillance cameras.
- When choosing a Wi-Fi router, you need to pay attention to which standards it supports. The more modern the standard, the higher the performance characteristics, including data transfer speed.
- It’s better to buy routers that support operation in two frequency bands. This way they can switch between them, choosing where network conditions are better.
- If the office has equipment that needs to be provided with the highest possible data transfer speed, such as a server, the router should be equipped with LAN ports with gigabit throughput for wired connection.
- The quality of the wireless network signal depends on radio interference and obstacles: furniture and walls. The number of connected devices is also important. If you need to create seamless coverage over a large area with load-bearing partitions and connect several dozen units of office equipment, it’s better to purchase a Mesh system.











Leave a Reply