Mold exposure significantly worsens asthma, heightening respiratory distress and asthma attack risks. Mold spores inflame airways, leading to symptoms like coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and breath shortness. Does mold cause asthma? Mold serves as a potent asthma trigger in sensitive individuals. Preventing mold growth involves controlling humidity, improving ventilation, and promptly addressing leaks. Properly managing indoor air quality can mitigate these risks. Understanding the link between mold and asthma highlights the crucial impact of environmental factors on respiratory health. Further insights await on the intricate relationship and effective prevention strategies.
Key Takeaways
– Mold exposure exacerbates asthma symptoms.
– Inhalation of mold spores triggers airway inflammation.
– Mold acts as a potent asthma trigger.
– High humidity levels promote mold growth.
– Proper ventilation helps manage mold-induced asthma.
Read Also:- Health Care
The Impact of Mold on Asthma
Mold exposure can exacerbate asthma symptoms, leading to increased respiratory distress and a heightened risk of asthma attacks. For individuals with mold spore sensitivity, the presence of mold in indoor environments can trigger inflammation in the airways, worsening asthma symptoms. The inhalation of mold spores can irritate the respiratory tract, causing coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath. These symptoms can be particularly severe in individuals already diagnosed with asthma, as the presence of mold can act as a potent asthma trigger.
Research has shown a clear link between mold exposure and asthma exacerbation. A study published in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine found that individuals with asthma who were exposed to mold had a higher likelihood of experiencing asthma symptoms and exacerbations. This highlights the importance of addressing mold issues in indoor environments to reduce the risk of asthma attacks and improve respiratory health.
Common Symptoms of Mold Exposure
When exposed to mold, you may experience symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, and shortness of breath. These respiratory issues can worsen in individuals with asthma or other respiratory conditions.
It’s crucial to recognize these common symptoms of mold exposure to address the potential health risks associated with mold in indoor environments.
Mold-Induced Asthma Symptoms

Mold exposure can trigger a range of symptoms in individuals with asthma, highlighting the potential link between mold and exacerbation of respiratory issues. Mold spore sensitivities play a significant role in aggravating asthma symptoms, with common manifestations including coughing, wheezing, chest tightness, and shortness of breath.
Managing mold-induced asthma involves reducing exposure to environmental allergens and triggers. It’s crucial to address any mold growth in indoor spaces promptly, as mold spores can act as potent irritants for sensitive individuals. By implementing proper ventilation, reducing humidity levels, and promptly fixing any leaks or water damage, individuals with asthma can better manage their symptoms and improve their overall respiratory health.
Respiratory Issues From Mold
To understand the impact of mold on respiratory health, it’s crucial to recognize the common symptoms that individuals may experience from mold exposure. Mold spore dispersion can lead to a range of respiratory issues, including coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and chest tightness.
These symptoms are often exacerbated in individuals with asthma, as mold can act as a potent trigger for asthma exacerbation. Research suggests that prolonged mold exposure can also contribute to the development of asthma in individuals previously unaffected by the condition.
Therefore, it’s essential to address any signs of respiratory distress promptly and consider investigating potential mold sources in indoor environments to mitigate the risk of respiratory problems associated with mold exposure.
Asthma Triggers in Indoor Environments
Indoor environments harbor a multitude of potential asthma triggers that can exacerbate respiratory symptoms and contribute to the overall burden of asthma management. Mold allergies are a common trigger, with mold spores in the air causing reactions in sensitive individuals. Prevention strategies such as controlling moisture levels, fixing leaks promptly, and improving ventilation can help reduce mold growth and minimize its impact on asthma.
In asthma management, humidity plays a crucial role as high humidity levels can create an ideal environment for mold to thrive. Dust mites, another common trigger, also flourish in humid conditions. Regularly cleaning and dusting your home, washing bedding in hot water, and using allergen-proof mattresses and pillow covers are essential steps to mitigate dust mite-related asthma symptoms.
Additionally, pet dander, tobacco smoke, strong odors, and air pollutants like volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from cleaning products can all trigger asthma symptoms. Being mindful of these indoor triggers and taking proactive measures to minimize their presence can significantly improve respiratory health and overall quality of life for individuals managing asthma.
Understanding Respiratory Health Risks
Respiratory health risks encompass a range of factors that can impact breathing and lung function, requiring a comprehensive understanding to effectively manage and mitigate potential complications.
Respiratory conditions such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and bronchitis are influenced by various environmental factors. Exposure to mold, dust mites, tobacco smoke, air pollution, and allergens can exacerbate these conditions, leading to worsened symptoms and decreased lung function over time.
Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions are particularly vulnerable to the effects of poor indoor air quality. Mold, in particular, can trigger asthma attacks and allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Understanding these risks is crucial for implementing preventive measures and maintaining respiratory health. By reducing exposure to indoor pollutants, improving ventilation, and ensuring proper humidity levels, individuals can help mitigate the impact of environmental factors on respiratory health.
Regular monitoring of indoor air quality and seeking medical advice for respiratory symptoms are essential steps in managing these risks effectively.
Mold Prevention Techniques for Asthma
Exploring practical strategies to prevent mold growth can significantly benefit individuals with asthma by reducing triggers for respiratory symptoms. Mold spore prevention is crucial for maintaining good indoor air quality and overall respiratory health.
To manage asthma effectively, it’s essential to control allergens like mold that can exacerbate symptoms. Start by keeping humidity levels below 50% to inhibit mold growth. Use dehumidifiers in damp areas like basements and bathrooms, and ensure proper ventilation in kitchens and bathrooms to prevent moisture buildup.
Regularly inspect and repair any leaks in pipes, roofs, or windows to prevent water intrusion that promotes mold growth. Clean and dry any damp areas promptly, as mold can start growing within 24-48 hours. Consider using mold-resistant products in areas prone to moisture, such as bathrooms.
Identifying Mold in Your Home
To identify mold in your home, you can employ various detection methods such as visual inspection, mold testing kits, or professional assessments.
Common locations where mold thrives include damp basements, bathrooms, kitchens, and areas with water leaks or high humidity levels.
Understanding the health risks associated with mold exposure underscores the importance of promptly addressing any mold issues in your living space.
Mold Detection Methods
When looking for mold in your home, utilizing various detection methods can help identify potential problem areas. Mold spores are microscopic and can be present in the air, making them hard to detect visually.
One effective method is using allergy testing, which can pinpoint specific mold types causing reactions. You can also use mold testing kits available in hardware stores to collect samples for analysis. These kits can detect mold growth even if it’s hidden behind walls or ceilings.
Another option is hiring professionals who use advanced tools like moisture meters and infrared cameras to locate hidden mold. By combining these methods, you can accurately identify mold in your home and take appropriate actions to address the issue promptly.
Common Mold Locations
Identifying common mold locations in your home requires a systematic approach that considers areas prone to moisture accumulation and poor ventilation. Common places where mold growth is often found include bathrooms, kitchens, basements, and areas near leaky pipes or windows.
These areas provide the damp environment that mold spores need to thrive. To effectively prevent mold growth, it’s crucial to address any water leaks promptly, ensure proper ventilation in humid areas, and regularly inspect and clean areas susceptible to mold.
Implementing these practices can significantly reduce the risk of mold growth in your home, promoting a healthier living environment for you and your family.
Stay vigilant and proactive in maintaining a mold-free home to safeguard against potential health hazards.
Health Risks Associated
Exploring the presence of mold in your home demands a keen awareness of the potential health risks associated with its growth. Here are four key health risks you should consider:
1. Respiratory Issues: Mold spores can trigger allergies and asthma symptoms, leading to difficulty breathing.
2. Skin Irritation: Contact with mold can cause skin rashes, itchiness, or other dermatological problems.
3. Infections: Certain molds produce mycotoxins that can lead to infections in individuals with weakened immune systems.
4. Neurological Symptoms: Prolonged exposure to mold has been linked to cognitive issues, mood changes, and fatigue.
To safeguard your health, prioritize mold prevention strategies and work closely with healthcare providers for effective asthma management.
Treatment Options for Mold-Induced Asthma
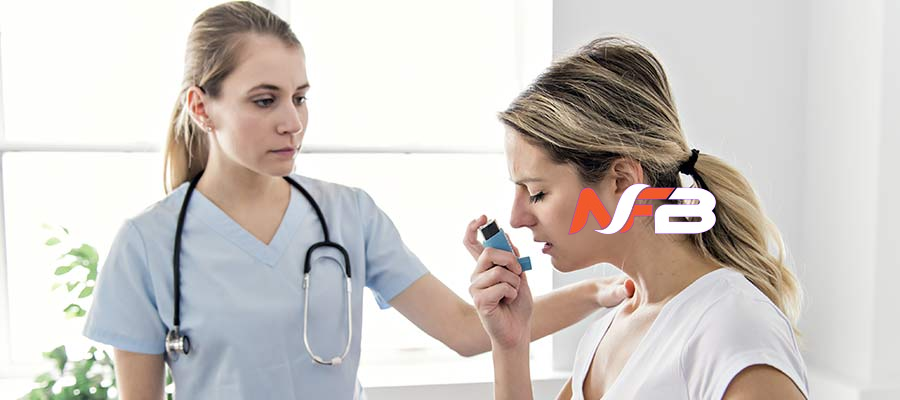

Considering the various treatment options available for mold-induced asthma, it’s essential to prioritize comprehensive management strategies that address both the underlying asthma condition and the mold exposure to effectively control symptoms and improve quality of life.
Medication management plays a crucial role in controlling asthma symptoms triggered by mold exposure. Your healthcare provider may prescribe bronchodilators to help open up the airways and corticosteroids to reduce inflammation. Allergy testing can identify specific mold allergens that exacerbate your asthma, enabling targeted treatment.
In addition to medication, environmental control is paramount. Implement measures such as using air purifiers, reducing humidity levels, and fixing any water leaks to minimize mold growth. Developing an asthma action plan with your healthcare provider can guide you on how to manage asthma symptoms during mold exposure episodes, empowering you to take timely and effective actions to prevent exacerbations.
The Role of Allergens in Asthma
To understand the impact of allergens on asthma, it’s crucial to recognize how specific triggers can exacerbate respiratory symptoms in individuals with this condition. Allergen management and asthma control are paramount in maintaining respiratory health.
Here are four key points to consider:
1. Identification of Triggers: Understanding the specific allergens that trigger your asthma symptoms is crucial. Common allergens include dust mites, pet dander, pollen, and mold. Identifying and minimizing exposure to these allergens can significantly improve asthma control.
2. Mold Exposure and Asthma: Mold exposure can worsen respiratory health, leading to increased asthma symptoms and exacerbations. Managing indoor humidity levels, promptly addressing water leaks, and ensuring proper ventilation are essential in reducing mold growth and subsequent asthma complications.
3. Allergen Avoidance Strategies: Implementing allergen avoidance strategies such as using allergen-proof bedding, regularly cleaning carpets and upholstery, and keeping pets out of bedrooms can help minimize allergen exposure and improve asthma control.
4. Regular Monitoring and Maintenance: Regularly monitoring indoor air quality, maintaining HVAC systems, and using air purifiers can aid in reducing allergens and promoting better respiratory health for individuals with asthma.
Improving Indoor Air Quality
Improving indoor air quality is essential for reducing allergens and promoting respiratory health in individuals with asthma. To achieve this, consider using air purifiers and ensuring proper ventilation in your home. Air purifiers can help eliminate mold spores, dust mites, pet dander, and other allergens that can trigger asthma symptoms. Proper ventilation, such as opening windows when possible or using exhaust fans, can help circulate fresh air and prevent the buildup of indoor pollutants.
Humidity control is another crucial aspect of indoor air quality management. Keeping humidity levels between 30-50% can inhibit mold growth and reduce the presence of dust mites. Consider using dehumidifiers in damp areas like basements or bathrooms to maintain optimal humidity levels.
Filtration is also key to improving air quality. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters can capture small particles, including mold spores and pollen, preventing them from circulating in the air. Regularly changing filters in HVAC systems can ensure they function effectively in trapping airborne irritants. By implementing these strategies, you can create a healthier indoor environment that supports your respiratory well-being.
Read Also:- wellhealthorganic stress management
Conclusion
In conclusion, the link between mold and asthma is a significant concern for individuals with respiratory issues. Mold exposure can exacerbate asthma symptoms and trigger respiratory distress. Understanding the impact of mold on asthma, identifying mold in indoor environments, and implementing prevention techniques are crucial steps in managing asthma triggers.
Improving indoor air quality and seeking treatment options for mold-induced asthma can help individuals better control their respiratory health and overall well-being.












Leave a Reply